self tapping screw measurement
Understanding Self-Tapping Screw Measurement
Self-tapping screws are innovative fasteners designed to create their own mating thread in the material they are driven into, making them essential components in various applications, from construction to electronics. To ensure efficient use and optimal performance, it is crucial to understand how to measure self-tapping screws accurately. This article will explore the key aspects of measuring these screws, focusing on their dimensions, types, and applications.
Types of Self-Tapping Screws
Before delving into measurement techniques, it’s important to recognize the types of self-tapping screws available. The most common types include
1. Thread-forming screws These screws displace material to create threads without cutting into the base material. They are typically used in softer substances like plastics. 2. Thread-cutting screws These screws actually cut into the material, making them suitable for harder materials like metals. They often feature sharp cutting edges that facilitate the threading process.
3. Self-drilling screws These are designed with a drill bit tip that allows them to penetrate the material, creating both a hole and a thread in one action. They are often used in metal-to-metal applications.
Key Measurements
When measuring self-tapping screws, several dimensions need to be considered
1. Diameter The diameter is a critical measurement that refers to the width of the screw shaft. It is usually measured in inches or millimeters. For example, a screw with a diameter of 10 corresponds to a specific inch measurement that is standardized.
2. Length The length of the screw is measured from the underside of the head to the tip of the screw. This measurement determines how deep the screw can be inserted into the material, which is vital for ensuring secure fastening.
self tapping screw measurement
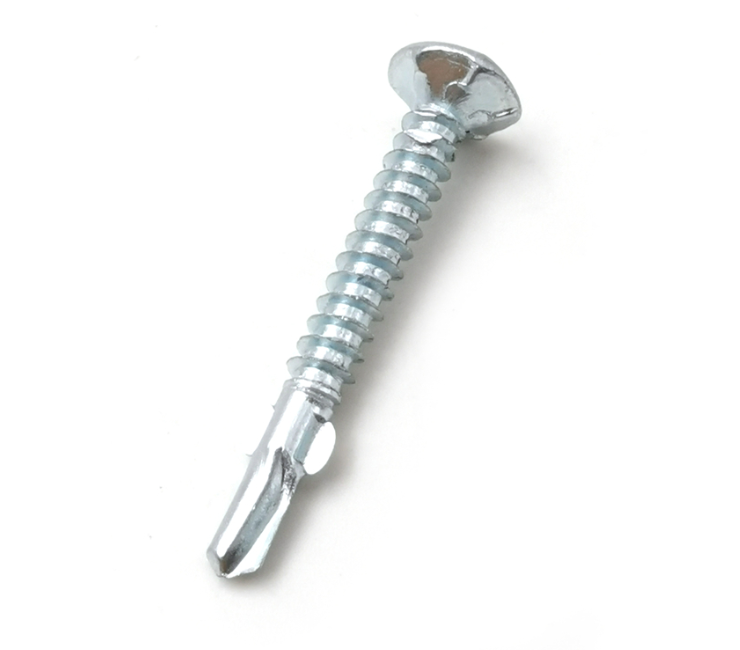
3. Head Style The head of the screw can vary, including flat, pan, or oval shapes. Measuring the head style and diameter is important, particularly for ensuring compatibility with fastening tools and aesthetics.
4. Thread Pitch This refers to the distance between the threads and is usually measured in threads per inch (TPI) or in metric terms (millimeters). Adjusting the thread pitch can change the holding power of the screw.
5. Material and Coating While not strictly a dimensional measurement, understanding the material (steel, stainless steel, etc.) and any coatings (like zinc plating) can significantly affect the screw’s performance in various environments.
Measuring Tools
To measure self-tapping screws accurately, several tools can be employed
- Caliper A caliper is an essential tool for measuring the diameter and length of screws. Digital calipers offer precision and ease of reading.
- Thread Gauge This tool helps in determining the thread pitch, which is crucial for selecting the right screw for the job.
Conclusion
Understanding the measurement of self-tapping screws is vital for engineers, manufacturers, and DIY enthusiasts alike. By accurately measuring diameter, length, thread pitch, and head style, one can ensure the selection of the right screw for the intended application. Proper measurement not only enhances the effectiveness of the fastening process but also contributes to the safety and durability of construction and manufacturing projects. Whether you’re working on a simple home repair or a complex engineering task, mastering screw measurements will lead to better outcomes and improved performance in your projects.
-
Top Choices for Plasterboard FixingNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatility of Specialty WashersNewsDec.26,2024
-
Secure Your ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Essential Screws for Chipboard Flooring ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Choosing the Right Drywall ScrewsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Black Phosphate Screws for Superior PerformanceNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatile Choice of Nylon Flat Washers for Your NeedsNewsDec.18,2024










