Fev . 11, 2025 10:51
Back to list
machine screw vs self tapping
When it comes to fastening materials together, two types of screws often dominate the conversation machine screws and self-tapping screws. Understanding the differences between these two can be crucial for ensuring the longevity and strength of your construction or engineering project. Each screw type has unique characteristics, applications, and benefits, making them suitable for specific tasks.
The primary benefit of self-tapping screws is their ease of use and efficiency in installation. By cutting their own threads, these screws provide a tight fit, reducing the chances of loosening over time. They are particularly useful in scenarios where materials are layered or when accessing both sides of a joint is challenging. Moreover, they are cost-effective for production environments where rapid assembly is required. A key consideration is the material of both the screw and the substrate. Machine screws, often made from hardened steel, stainless steel, or brass, must match the material properties of the substrate for optimal performance, particularly where environmental factors such as corrosion are concerned. Self-tapping screws, however, must be chosen carefully to avoid potential issues like overtightening or stripping the material during installation. In conclusion, selecting between machine screws and self-tapping screws hinges on specific application requirements. For projects demanding precise alignment and high-strength connections, machine screws are ideal. Conversely, for applications where speed, efficiency, and the ability to self-thread are priorities, self-tapping screws offer unparalleled convenience. Understanding these differences and choosing the appropriate type based on material, environmental conditions, and structural demands can dramatically impact the success and durability of any project. Experts advise that consultation with professionals or conducting rigorous testing can provide the necessary assurance that the chosen fastener will meet all performance expectations. This due diligence not only optimizes functionality but also ensures safety and compliance with industry standards.
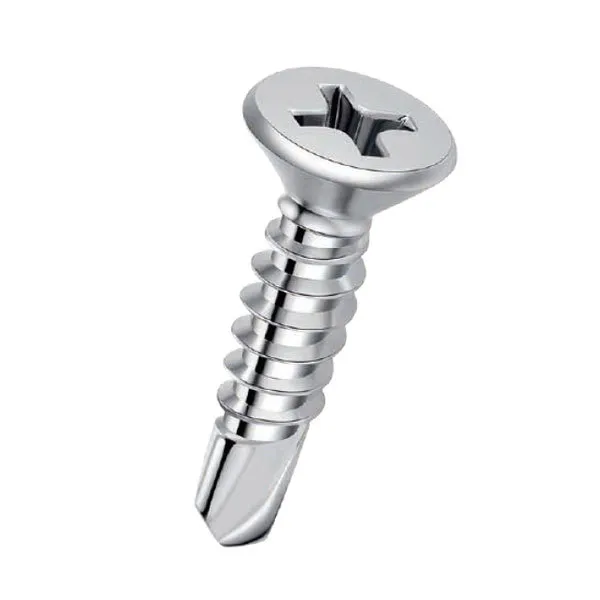

The primary benefit of self-tapping screws is their ease of use and efficiency in installation. By cutting their own threads, these screws provide a tight fit, reducing the chances of loosening over time. They are particularly useful in scenarios where materials are layered or when accessing both sides of a joint is challenging. Moreover, they are cost-effective for production environments where rapid assembly is required. A key consideration is the material of both the screw and the substrate. Machine screws, often made from hardened steel, stainless steel, or brass, must match the material properties of the substrate for optimal performance, particularly where environmental factors such as corrosion are concerned. Self-tapping screws, however, must be chosen carefully to avoid potential issues like overtightening or stripping the material during installation. In conclusion, selecting between machine screws and self-tapping screws hinges on specific application requirements. For projects demanding precise alignment and high-strength connections, machine screws are ideal. Conversely, for applications where speed, efficiency, and the ability to self-thread are priorities, self-tapping screws offer unparalleled convenience. Understanding these differences and choosing the appropriate type based on material, environmental conditions, and structural demands can dramatically impact the success and durability of any project. Experts advise that consultation with professionals or conducting rigorous testing can provide the necessary assurance that the chosen fastener will meet all performance expectations. This due diligence not only optimizes functionality but also ensures safety and compliance with industry standards.
Latest news
-
Top Choices for Plasterboard FixingNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatility of Specialty WashersNewsDec.26,2024
-
Secure Your ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Essential Screws for Chipboard Flooring ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Choosing the Right Drywall ScrewsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Black Phosphate Screws for Superior PerformanceNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatile Choice of Nylon Flat Washers for Your NeedsNewsDec.18,2024
Related News










