Suppliers for 1/4-20 Self Tapping Screws and Their Optimal Hole Size Specifications
Understanding 1/4-20 Self Tapping Screw Hole Sizes A Guide for Suppliers
When it comes to assembly and construction, fasteners play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and durability of structures. Among these fasteners, self-tapping screws are particularly popular due to their ability to create their own holes as they are driven into materials. A common specification for these screws is the 1/4-20 size, which indicates both the diameter and threads per inch. Understanding the hole size for 1/4-20 self-tapping screws is essential for suppliers aiming to provide the right products for various applications.
What Does 1/4-20 Mean?
The term 1/4-20 describes a screw with a nominal diameter of 1/4 inch and 20 threads per inch (TPI). This sizing standard allows manufacturers and suppliers to classify screws clearly and ensures compatibility with various applications. The self-tapping feature of these screws means they are designed to create threads in the material they are driven into, making them ideal for materials that are soft or need a secure, snug fit.
Importance of Hole Size
The hole size is critical for ensuring the proper function of a self-tapping screw. If the hole is too large, the screw may not grip properly, leading to potential loose fittings and, eventually, structural failure. Conversely, if the hole is too small, it can cause the screw to break or the material to split during insertion. Therefore, understanding the appropriate hole size for a 1/4-20 self-tapping screw is vital for suppliers who want to meet customer needs effectively.
Recommended Hole Sizes
For 1/4-20 self-tapping screws, the recommended pilot hole size is typically around 0.201 inches in diameter. This pilot hole allows the screw to tap threads into the material effectively while reducing stress on the screw and the surrounding material. When working with softer materials, such as wood or plastic, this pilot hole ensures that the screw can penetrate easily and create a secure fit without unnecessary damage.
1/4-20 self tapping screw hole size suppliers
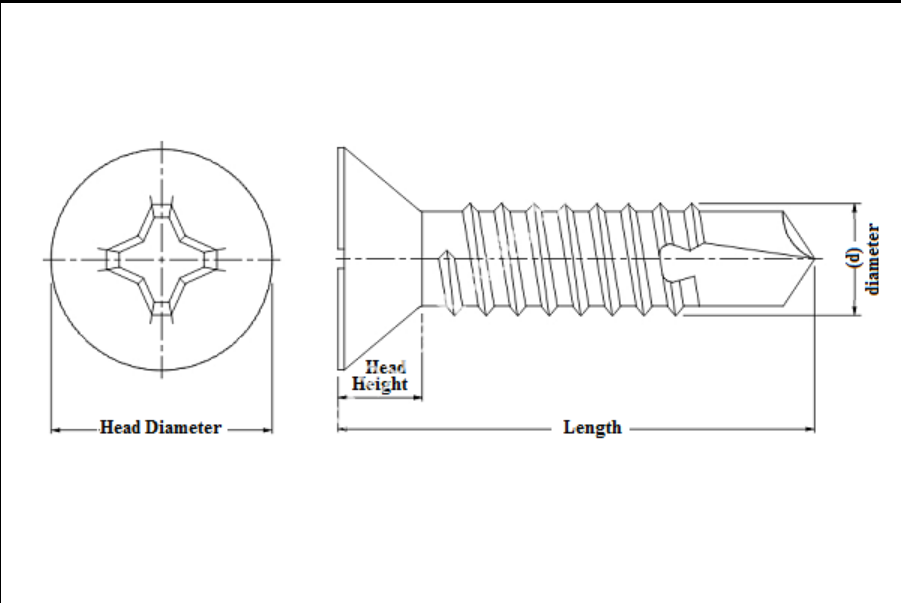
When working with harder materials, such as metal, suppliers may recommend a slightly larger pilot hole, often in the range of 0.250 inches, to ensure that the screw can be inserted without excessive force, thereby avoiding potential breakage and maintaining the structural integrity of the assembly.
Factors Affecting Hole Size
Several factors can influence the optimal hole size for 1/4-20 self-tapping screws
1. Material Type The density and hardness of the material being fastened will affect the required hole size. Softer materials often require smaller pilot holes compared to harder materials. 2. Screw Length The length of the screw can also impact the choice of hole size. Longer screws may need more precise hole sizes to ensure they engage properly in the substrate.
3. Thread Design Different self-tapping screws may have varied thread designs that can require different hole sizes for optimal performance.
4. Application The specific application can dictate the required hole size as well. For example, high-vibration applications may demand tighter tolerances to ensure screws do not loosen over time.
Conclusion
For suppliers of 1/4-20 self-tapping screws, understanding the importance of hole size is paramount. Providing accurate information about the recommended pilot hole dimensions can greatly affect the performance and reliability of the screws in various applications. By educating customers about these technical specifications, suppliers not only enhance their credibility but also promote safer and more effective usage of self-tapping screws in construction and assembly. Ensuring proper measurements will allow customers to achieve durable results, ultimately leading to satisfaction and repetitive business.
-
Top Choices for Plasterboard FixingNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatility of Specialty WashersNewsDec.26,2024
-
Secure Your ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Essential Screws for Chipboard Flooring ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Choosing the Right Drywall ScrewsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Black Phosphate Screws for Superior PerformanceNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatile Choice of Nylon Flat Washers for Your NeedsNewsDec.18,2024










