Optimal Hole Size for OEM M4 Self-Tapping Screws for Enhanced Performance and Reliability
Understanding OEM M4 Self-Tapping Screw Hole Size
When it comes to assembling materials in engineering and manufacturing, the consideration of screw sizes and hole dimensions is crucial. Among the various options available, the M4 self-tapping screw stands out for its versatility and efficiency. This article delves into the specifications concerning the hole size required for M4 self-tapping screws, emphasizing their significance in various applications.
What Are M4 Self-Tapping Screws?
M4 self-tapping screws are typically used in light to medium-duty applications. The M designation refers to the metric thread standard, with the 4 indicating a nominal diameter of 4 mm. Self-tapping screws are designed with threads that can cut into materials, allowing them to create their own mating thread when driven into a pre-drilled hole. This unique ability makes them invaluable in multiple industries, including automotive, construction, and electronics.
Importance of Hole Size
Understanding the correct hole size for M4 self-tapping screws is essential for ensuring strong and durable assemblies. The hole must be appropriately sized to facilitate easy insertion of the screw while still providing sufficient material contact to create a strong thread. An incorrect hole size can lead to various issues, including poor fastening strength, material damage, or even screw failure.
Recommended Hole Size for M4 Screws
For M4 self-tapping screws, the standard pre-drilled hole size is typically specified as follows
oem m4 self tapping screw hole size
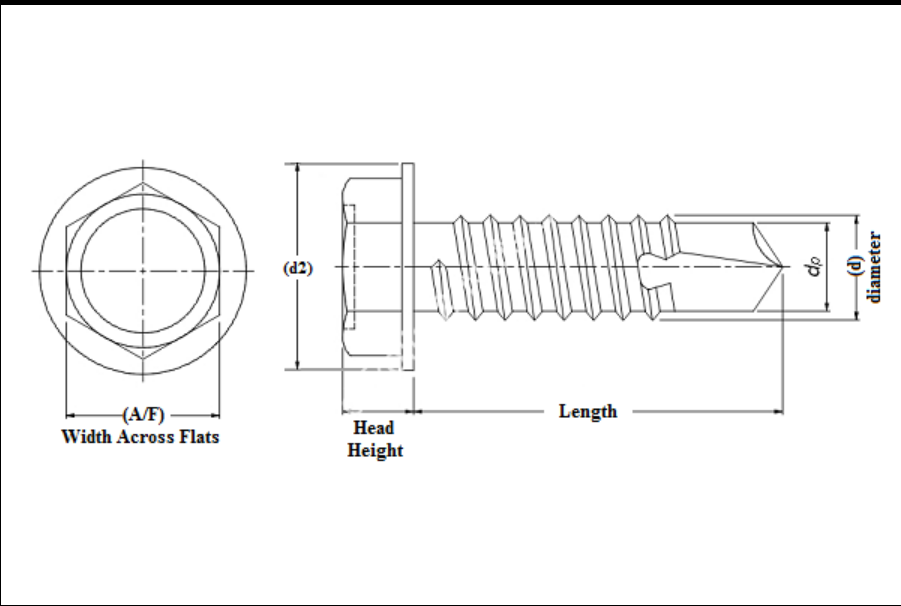
- For Soft Materials In materials such as plastic or soft wood, a pilot hole of approximately 3.2 mm (0.126 inches) is recommended to allow for effective screwing without excessive resistance. - For Harder Materials When dealing with metal or hardwood, a slightly smaller hole, usually around 2.8 mm to 3.0 mm (0.110 to 0.118 inches), may be necessary. This slight reduction in size allows the screw threads to engage effectively and create a strong bond.
Considerations When Choosing Hole Sizes
When determining the size of the hole for an M4 self-tapping screw, several factors need to be considered
1. Material Type The nature of the material being fastened will significantly influence the ideal hole size. Softer materials will allow for larger holes to mitigate excessive torque, whereas harder materials may require tighter fits. 2. Thread Design The specific threading on the screw can impact how well it grips the material. Design variations may necessitate adjustments in the hole diameter.
3. Environment In applications subject to moisture or corrosion, the choice of materials in both the screw and the material being fastened can affect the hole size and the overall assembly.
4. Load Requirements The expected load on the assembly also dictates the hole size. Higher loads may necessitate tighter hole tolerances to prevent failure.
Conclusion
Understanding the appropriate hole size for M4 self-tapping screws is essential for achieving optimal performance in various applications. By taking into account the material type, screw design, environmental conditions, and load requirements, manufacturers and engineers can ensure reliable and durable assemblies. Proper specification of hole sizes not only enhances the integrity of fastening but also improves the efficiency of the assembly process. As technology and materials continue to evolve, staying informed about such specifications becomes increasingly important for achieving excellence in engineering and manufacturing.
-
Top Choices for Plasterboard FixingNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatility of Specialty WashersNewsDec.26,2024
-
Secure Your ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Essential Screws for Chipboard Flooring ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Choosing the Right Drywall ScrewsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Black Phosphate Screws for Superior PerformanceNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatile Choice of Nylon Flat Washers for Your NeedsNewsDec.18,2024










