Comparison of ODM Wave Washers and Spring Washers for Performance Efficiency
ODM Wave Washer vs. Spring Washer A Comprehensive Comparison
In the world of mechanical engineering and design, washers play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and functionality of assemblies. Among the various types of washers, the ODM wave washer and the traditional spring washer are two popular choices. Both serve to provide tension and accommodate thermal expansion, but they come with different design features, applications, and advantages. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between ODM wave washers and spring washers.
Design Differences
The most significant distinction between ODM wave washers and spring washers lies in their design. ODM wave washers, also known as wave springs, feature a series of wave-like ridges that create a spring effect. They are generally flat and made from materials such as stainless steel, ensuring durability and resistance to corrosion. The wave design allows for a compact fit, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
In contrast, traditional spring washers, which are often helical in shape, are thicker and more voluminous. These washers function by exerting a preloaded force, which helps maintain tension in the assembly. While spring washers can also be made from various materials, they typically require more space compared to wave washers.
Performance and Functionality
When it comes to performance, both types of washers excel in providing mechanical stability and mitigating the effects of vibrations. However, their operational characteristics differ.
odm wave washer vs spring washer
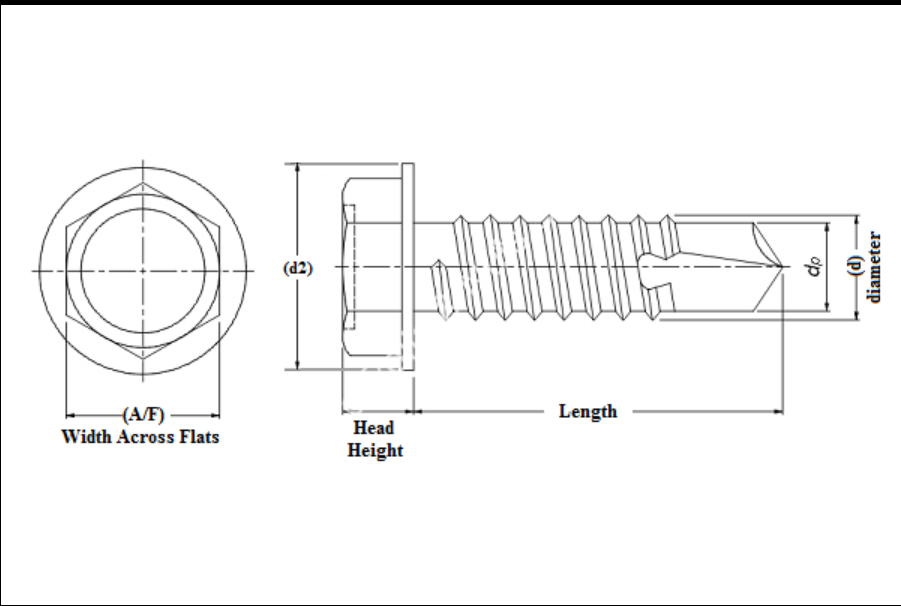
Wave washers distribute load evenly across their surface, providing a consistent and stable pressure. This feature makes them particularly suitable for applications where precise torque is necessary, such as in automotive or aerospace components. Their ability to handle lateral movement also makes them effective in dynamic applications.
On the other hand, spring washers are best suited for applications requiring high levels of clamping force. They are designed to resist loosening under vibration, making them a popular choice in heavy machinery and structural applications. However, their thickness might limit their use in compact assemblies.
Installation and Maintenance
In terms of installation, ODM wave washers provide an advantage due to their lower profile and lighter weight. They can easily fit into tighter spaces, facilitating straightforward assembly processes. Additionally, their design often leads to reduced installation time, translating to cost savings in manufacturing.
Spring washers, while effective, may require more careful alignment during installation to ensure optimal performance. Their bulkier design can complicate the assembly process in constrained spaces. Maintenance is relatively low for both types; however, wave washers have the edge in terms of longevity and reduced wear, thanks to their unique design that minimizes friction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both ODM wave washers and spring washers have their merits and are suitable for different applications depending on the specific requirements of a project. Wave washers are ideal for tight spaces and consistent load distribution, while spring washers are preferred for applications needing higher clamping forces and resistance to loosening. Selecting the appropriate washer ultimately comes down to understanding the unique demands of the application at hand. By considering factors such as design constraints, performance needs, and maintenance requirements, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance the reliability and longevity of their designs.
-
Top Choices for Plasterboard FixingNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatility of Specialty WashersNewsDec.26,2024
-
Secure Your ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Essential Screws for Chipboard Flooring ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Choosing the Right Drywall ScrewsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Black Phosphate Screws for Superior PerformanceNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatile Choice of Nylon Flat Washers for Your NeedsNewsDec.18,2024










