Exploring Various Dimensions and Types of Self Tapping Screws for Your Projects and Applications
Understanding Self-Tapping Screw Dimensions and Their Applications
Self-tapping screws play a crucial role in various construction and manufacturing processes, providing a reliable solution for fastening materials without the need for pre-drilled holes. Understanding their dimensions and specifications is key for anyone looking to use them effectively in various applications.
What is a Self-Tapping Screw?
A self-tapping screw is a type of fastener that can tap its own hole as it is driven into materials. They are designed with a sharp point and threads along their shank that allow them to cut through the material as they are driven in, effectively creating their own mating threads. This feature makes them particularly useful in metal, plastic, and wood applications.
Key Dimensions of Self-Tapping Screws
When selecting self-tapping screws, it is essential to understand the various dimensions that define them
1. Length Measured from the top of the head to the tip of the screw, length is a vital dimension that influences the hold and strength of the fastening. Common lengths range from 1/2 inch to several inches, allowing for versatility in different materials and thicknesses.
2. Diameter The diameter of the screw, often referred to as the gauge, directly impacts the strength and application of the screw. The diameter is typically specified in either standard or metric units. Self-tapping screws range from sizes like 2 (approximately 0.086 inches) to 14 (approximately 0.194 inches), and metric sizes can range from M2 to M10.
self tapping screw dimensions products
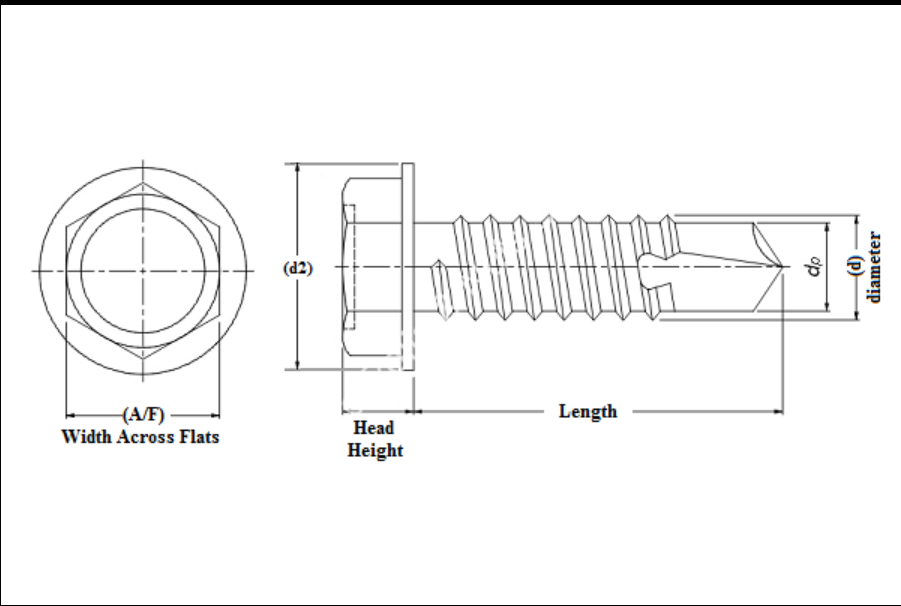
3. Thread Count This refers to the number of threads per inch (TPI) on the screw. Coarse threads, designed for quick installation in softer materials, provide a larger engagement area, while fine threads are used for greater strength in harder materials. A standard self-tapping screw may exhibit thread counts from 10 to 32, depending on its application.
4. Head Types Self-tapping screws come with various head styles, including pan, flat, round, and hex. Each head style is suited for different applications, with pan heads providing a larger bearing surface and flat heads being ideal for flush mounting. The choice of head type can affect the screw's ability to bear loads and its aesthetic appeal.
5. Point Types The design of the tip of a self-tapping screw also varies. Some common types include sharp points for metal application, blunt points for plastic, and drill points designed for use in harder materials. The choice of point affects how easily the screw penetrates the substrate and how clean the hole remains.
Selecting the Right Self-Tapping Screw
When choosing self-tapping screws, assess the material to be fastened, the environment (e.g., indoor vs. outdoor), and the load requirements. For instance, stainless steel screws are resistant to corrosion and are ideal for outdoor or humid applications, while zinc-plated screws provide good protection for indoor use.
It’s also crucial to consider the drive type; options like Phillips, slotted, and Torx drives affect the ease of installation and the potential for cam-out. Utilizing the correct tools and understanding the dimensions will ensure that the screws perform optimally for the intended application.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the dimensions and specifications of self-tapping screws is essential for effective selection and application. By considering length, diameter, thread count, head type, and point type, you can ensure that you choose the right screws for your projects, ultimately leading to stronger, more durable constructions. Whether you are a DIY enthusiast or a professional contractor, having a comprehensive knowledge of self-tapping screw dimensions will enhance your fastening strategies and ensure reliable results.
-
Top Choices for Plasterboard FixingNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatility of Specialty WashersNewsDec.26,2024
-
Secure Your ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Essential Screws for Chipboard Flooring ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Choosing the Right Drywall ScrewsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Black Phosphate Screws for Superior PerformanceNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatile Choice of Nylon Flat Washers for Your NeedsNewsDec.18,2024










