self tapping screw chart product
Understanding Self-Tapping Screws Your Guide to the Product Chart
Self-tapping screws are integral components in various construction and manufacturing projects, offering unique benefits over traditional screws. They are designed to tap their own hole as they are driven into a material, which eliminates the need for pre-drilling. This article explores the key aspects of self-tapping screws, including their benefits, types, materials, and how to interpret a product chart.
What Are Self-Tapping Screws?
Self-tapping screws are specialized fasteners that, as the name suggests, can create their own threads in the material they are being driven into. This capability makes them particularly valuable in applications where time and efficiency are crucial. They come in a variety of head types, thread designs, and sizes, making them versatile for numerous applications, including metalworking, woodworking, and construction.
Benefits of Self-Tapping Screws
1. Time Efficiency One of the most significant advantages of self-tapping screws is the reduction in installation time. Since they don't require pre-drilling, users can complete projects faster, leading to increased productivity.
2. Versatility Available in a range of materials and finishes, self-tapping screws can be used in various applications—from securing metal sheets to fastening wooden components.
3. Less Equipment Needed Without the need for drill bits, users can minimize the tools required on-site, simplifying logistics and reducing costs.
4. Stronger Hold The ability of self-tapping screws to form their own threads can provide a more robust grip in certain materials, especially thin metals, which reduces the chances of stripping or loosening over time.
Types of Self-Tapping Screws
Self-tapping screws generally fall into two main categories
1. Cutting Threads These screws have sharp threads designed to cut through the material. They are typically used in softer materials such as plastic or thin metal sheets.
self tapping screw chart product
2. Forming Threads These screws displace material to create threads instead of cutting. They are ideal for harder materials and can often deliver superior holding power.
Materials and Coatings
Self-tapping screws are crafted from various materials, including
- Steel The most common material, often galvanized or coated to resist corrosion. - Stainless Steel Ideal for applications where rust resistance is crucial, such as in outdoor projects. - Brass and Plastic Used for specific applications where lightweight or non-corrosive properties are desired.
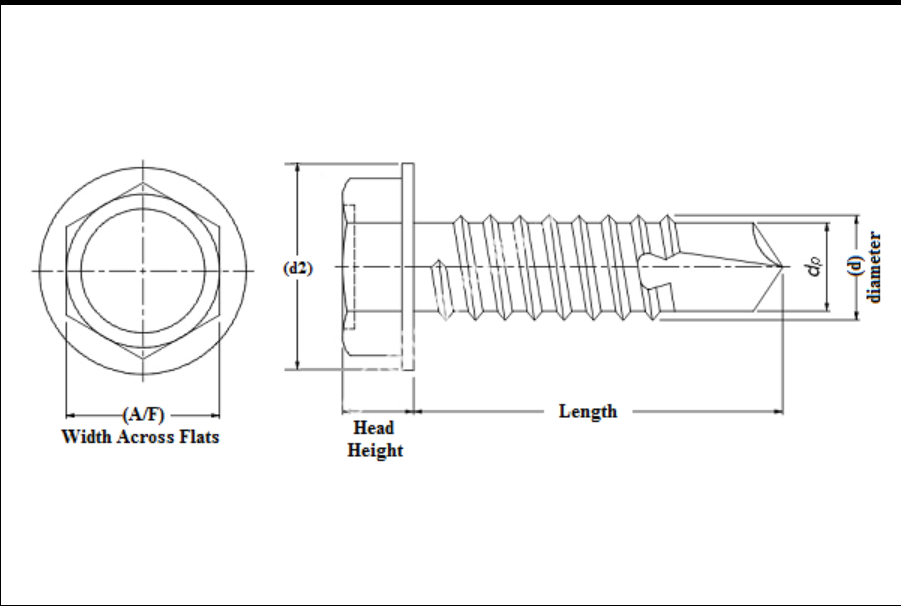
How to Read a Self-Tapping Screw Product Chart
When navigating a self-tapping screw product chart, key specifications to consider include
- Diameter and Length These measurements will dictate the screw's application. A larger diameter can provide greater holding strength, while length will influence how deeply the screw will embed into the material.
- Head Type Different head designs (e.g., Phillips, flat, hex) indicate the type of tools required for driving the screws.
- Thread Type Pay attention to whether the screw is a cutting or forming type, as this will impact the material compatibility.
- Material and Finish Choosing the right material and finish is essential for ensuring longevity and performance in your specific application.
Conclusion
Self-tapping screws are an efficient, versatile solution for various fastening needs. By understanding their features and how to interpret a product chart, you can choose the right screw for your project, ensuring durability and performance. Whether you're a hobbyist tackling DIY projects or a professional in construction, self-tapping screws can streamline your workflow and enhance the integrity of your builds.
-
Top Choices for Plasterboard FixingNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatility of Specialty WashersNewsDec.26,2024
-
Secure Your ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Essential Screws for Chipboard Flooring ProjectsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Choosing the Right Drywall ScrewsNewsDec.26,2024
-
Black Phosphate Screws for Superior PerformanceNewsDec.26,2024
-
The Versatile Choice of Nylon Flat Washers for Your NeedsNewsDec.18,2024










